hep c life expectancy
 What is the prognosis and life expectancy of hepatitis C patient? - Premier Medical Labs | Official Site | Reference Laboratory
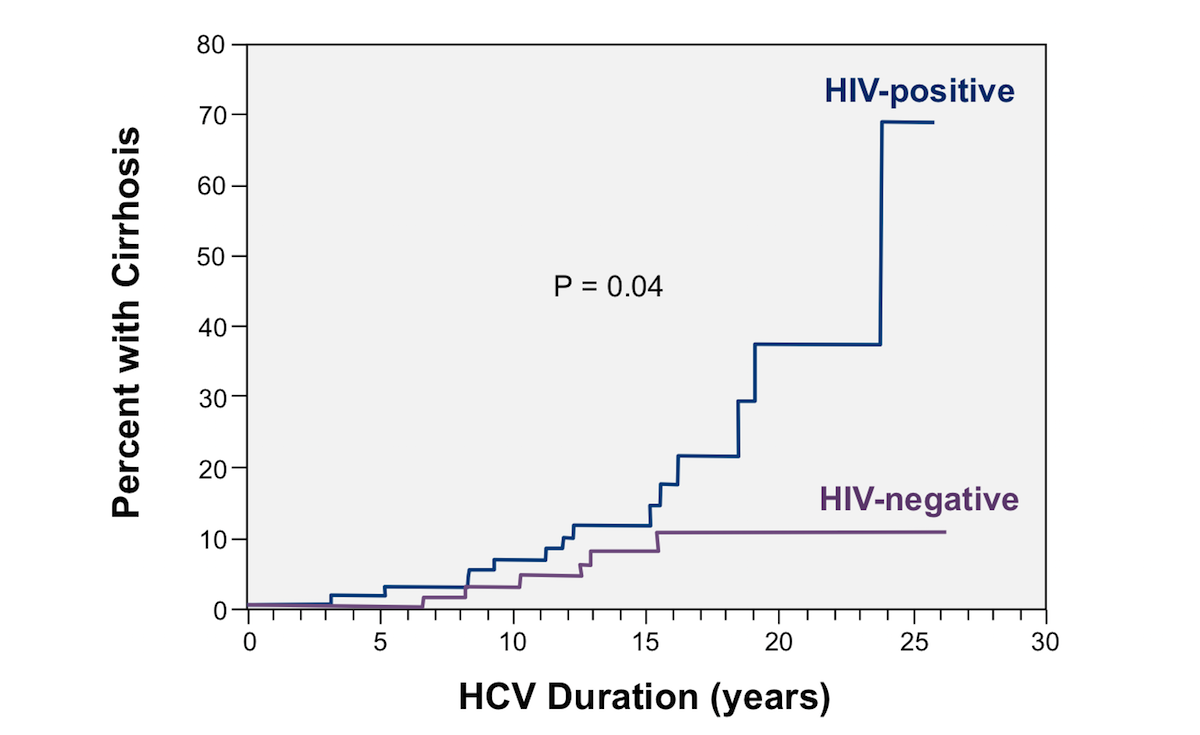
What is the prognosis and life expectancy of hepatitis C patient? - Premier Medical Labs | Official Site | Reference LaboratoryWhat can I expect with time with hepatitis C? Very understandably, almost everyone diagnosed with hepatitis C virus asks the same question: "What's going to happen to me?" Unfortunately, with HCV infection, it is very difficult for doctors to provide an answer. More than with most diseases, the course of HCV infection varies widely from person to person. In about 15 to 25 percent of people infected with the virus, their immune systems attack the virus and remove it, and they never know they were exposed. At the other end there are people who develop chronic infections and eventually severe liver diseases. Among people who carry the virus, but never show signs of problems, and others who have mild symptoms and some liver damage, but never develop a serious disease. Many factors affect the course of HCV infection Many factors affect the course of HCV infection How can a virus act so differently in different people? Researchers don't know all the answers. They know that men are more likely to develop serious liver problems than women. A published study found that between 13 and 46 percent of men developed cirrhosis (carreo of the liver) for a 30-year period of being infected with VHC. Only 1 to 29 percent of women developed the disease during the same period. Age when infection occurs also makes a difference in the course of the disease. The former in life people are infected, the lower the risk of severe complications of hepatitis C infection. Other health problems and HCVO infection problems and HCV infectionInfections with other viruses may worsen the VH prognosis. Many people are infected with hepatitis C and HIV/AIDS. Both viruses spread through shared needles. In a large European study, 33% of HIV-positive patients were also infected with HPV. When experts looked at known injecting drug users, they found that 75% of HIV positive patients also had hepatitis C viruses. Being infected with these two viruses seems to increase the risk of cirrhosis. In 2008, researchers found that after 20 years of infection, the risk of developing cirrhosis was 21 percent in people who were both HCV and HIV and 16 percent for those infected with HCV only. Certain lifestyle aspects also shape the course of HCV infection. Infected and alcohol-consuming people are more likely to develop liver problems than nondrinkers. Alcoholics have the greatest risk. A study conducted by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania found that alcohol really causes hepatitis C virus to multiply faster. Alcohol also decreases the effectiveness of alpha interferon, which is used to treat severe HV infections. In a report, Italian researchers showed that alcohol increases oxidative stress in the liver, generating unstable free radicals that can damage liver cells. Scientists speculate that "oxidative injury can be one of the mechanisms by which alcohol contributes to the progression of chronic hepatitis C." Other researchers have found a connection between hepatitis C infection and diabetes and type 2 obesity. In 2009, scientists at the Inova Fairfax Hospital Center for Liver Diseases analyzed health data for nearly 16,000 people, including some with hepatitis C. According to the results of the study, obesity and type 2 diabetes were associated with a higher mortality rate in patients with hepatitis C. This finding suggests that making lifestyle changes to avoid obesity and diabetes should be an important consideration for people with hepatitis C. Surprisingly, the level of virus in the blood, called viral load, does not help predict the course of hepatitis C. Some people with high viral levels do well. Others, with low levels of viruses, develop liver problems. Doctors use the test to measure how well the treatment is working, but not to make a prognosis. High levels of aminotransferase, a liver enzyme, are a sign that the disease is causing liver damage. But even this marker is not a perfect predictor. Up to 30% of patients with liver damage have normal aminotranferase levels. A Look at Numbers A Look at Numbers When patients ask, "What will happen to me?", the best answer doctors can give is to explain how the disease progresses in an average group of patients. Of every 100 people infected with HPV: 75 to 85 can develop long-term infection; of the following: As these numbers show, most people infected with hepatitis develop chronic infections. Among them, most have some signs of liver damage. But the numbers are also reassuring. Less than 7% of those who have chronic hepatitis C die from virus complications. That means for a vast majority of people, the virus is not fatal. In many, it causes nothing but mild symptoms such as fatigue. The Changing Table of HCV Infection The Changing Table of HCV Infection There are more good news coming out of clinical trials and pharmaceutical laboratories. The combined treatment used today is more effective than anything doctors could offer when the disease arose in 1989. Combination therapy can eliminate the virus in about half of all patients. Some combination treatments can do even better. A 2007 study of nearly 1,000 patients with hepatitis C showed a 99 percent healing rate after peginterferon and ribavirin treatment, with a number of patients who were left free of disease for seven years. The prognosis for people infected with HCV is brighter than ever. And it is likely to be brighter as doctors learn more effective combinations of existing drugs and as new drugs develop. ReferencesYounossi ZM, McCullough AJ. Metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic liver disease and hepatitis C virus: impact on disease progression and response to treatment. Liver International. 2009 Apr;29(4):617.American Medical Association. Healing rates becoming the norm for patients with hepatitis C. June 2007. http://www.ama-assn.org/amednews/2007/06/18/hlsc0618.htmThein HH, Yi Q, Dore GJ, Krahn MD. Estimates of progression rates of specific fibrosis in stages in the chronic infection of the hepatitis virus c: A meta-analysis and meta-regress. Hepatology. August 2008; 48(2): 418-431. Lauer, GL, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection, New England Journal of Medicine, July 5, 2001, pp 41-52Ho, W et al. Alcohol increases hepatitis C virus in human cells, Hepatology, July 2003, pp 57-65Pessione, F et al. Predictive factors of quinquennial survival in patients with excessive consumption of alcohol and cirrhosis. Effect of alcoholic hepatitis, smoking and abstinence, Liver International, Feb 2003, pp 45-53Seeff et al, The National Institutes of Health consensus Development Conference management of hepatitis C 2002, Clinical Liver Disease, Feb 2003, pp 261-87Cronic Hepatitis C: Disease Management, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/chronichepc/Thomas DL et al, The natural history of hepatitis C virus infection: host, viral and environmental factors, Journal of the American Medical Association, July 26, 2000, pp. 450-6Quaglio GL et al, Hepatitis Virus infection C: prevalence, predictive variables and prevention opportunities among drug users in Italy, Journal of Viral Hepatitis, Sep 2003, pp 394-400 Hisada et al., increase of hepatitis C viruses among injecting drug users infected with HIV and HTLV2, Journal of Infectious Diseases, September 15, 2003, pp 8 Thein HH, Yi Q, Dore GJ, Krahn MD. Natural history of hepatitis C virus infection in HIV-infected individuals and the impact of HIV on the age of antiretroviral therapy: a meta-analysis. AIDS. 1 October 2008; 22(15). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis C Frequently asked questions. http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/C/cFAQ.htm Copyright © 2020 HealthDay. All rights reserved. This site meets the HONcode standard for reliable health Wellness A-ZHealthDayConsumer Health News Professional News
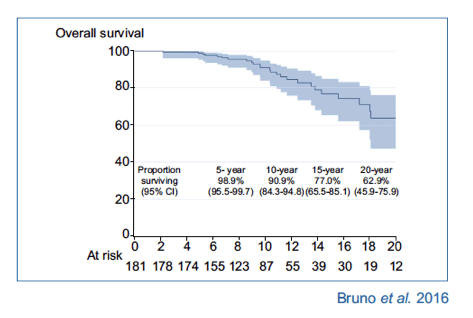
Survival of patients with HCV cirrhosis and sustained virologic response is similar to the general population.... Treated hepatitis C virus (HCV) cirrhotic patients can have normal life expectancy
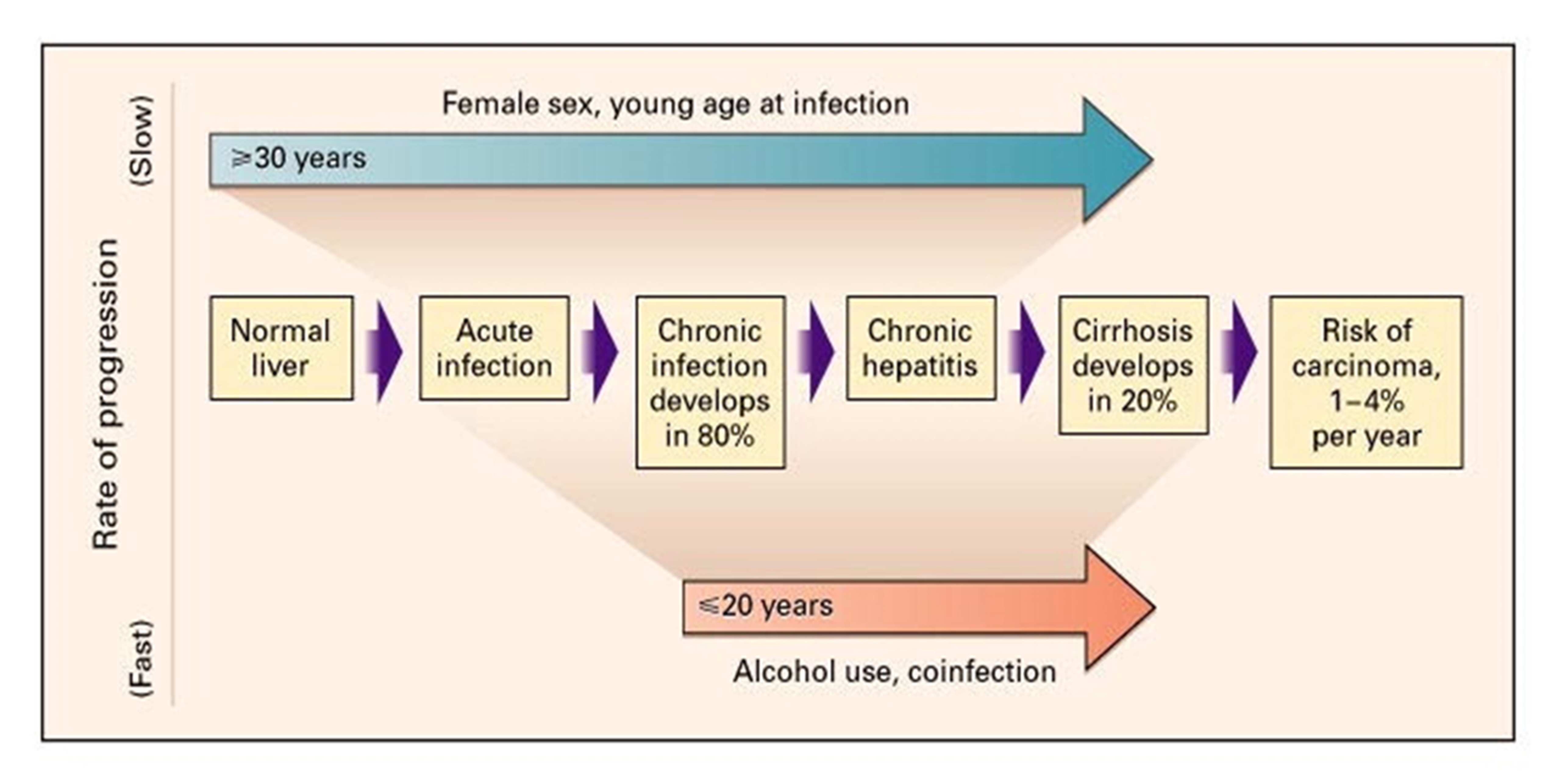
Hepatitis C

RACGP - Hepatitis C – an update
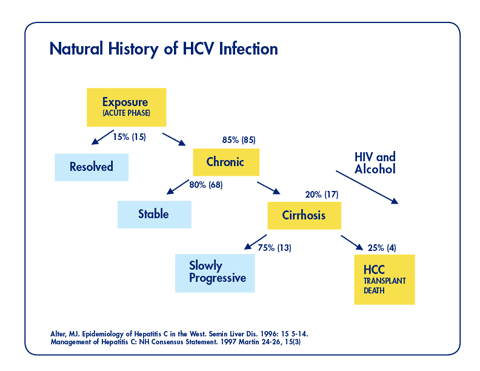
Hepatitis C Management and Hemodialysis | National Kidney Foundation

Can You Die from Hepatitis C? Prognosis and Life Expectancy

How long can you live with hepatitis C?
PLOS ONE: Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C in the Aged – Does It Impact Life Expectancy? A Decision Analysis
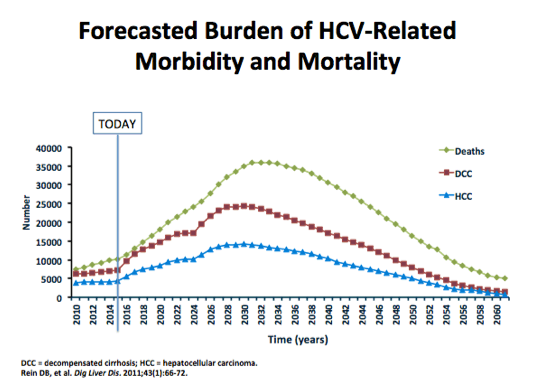
Cost Effectiveness of Hepatitis C Treatment
12 Possible Effects of Untreated Hepatitis C

Hep C's Drag on Life Expectancy - POZ

Hepatitis C - Wikipedia
Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C in the Aged – Does It Impact Life Expectancy? A Decision Analysis

Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Patients With Cancer: Impact on Clinical Trial Enrollment, Selection of Therapy, and Prognosis - Gastroenterology
Hepatitis C, a Leading Killer, Is Frequently Undiagnosed But Often Curable | UC San Francisco

Hepatitis C - Wikipedia
New Hepatitis C Treatments Are Paving The Way To Longer Life Expectancy
Core Concepts - Treatment of HCV in Persons with HIV Coinfection - Treatment of Key Populations and Unique Situations - Hepatitis C Online

Management of concomitant hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis C: a review

Hep C Takes 15 Years Off Life Span, Raises Death Risk 12-Fold - Hep

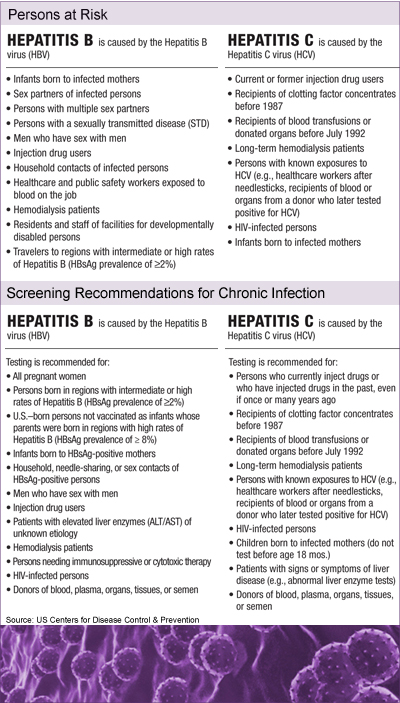
Hepatitis C Guidance 2019 Update: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases–Infectious Diseases Society of America Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection - Ghany - 2020 -
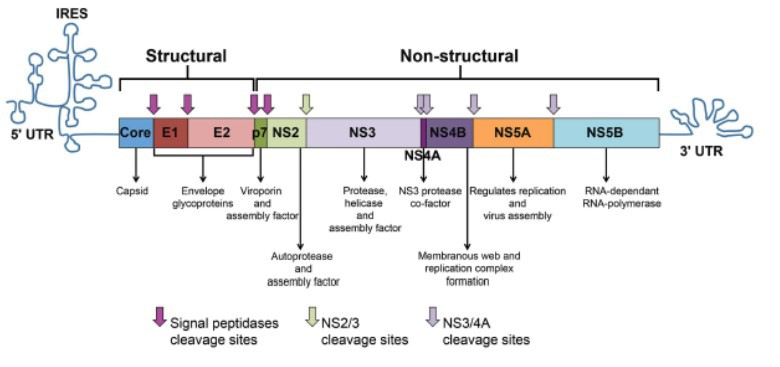
Hepatitis C and Chronic Kidney Disease: Overview of Evaluation and Management | National Kidney Foundation

Cost-Effectiveness of Access Expansion to Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Through Primary Care Providers - Gastroenterology

Management of concomitant hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis C: a review

Natural History of Hepatitis C Infection - Core Concepts

In a Critical State: Ongoing Barriers to Treatment for Hepatitis C Virus ( HCV) - The American Journal of Medicine

Take Control of Hep C
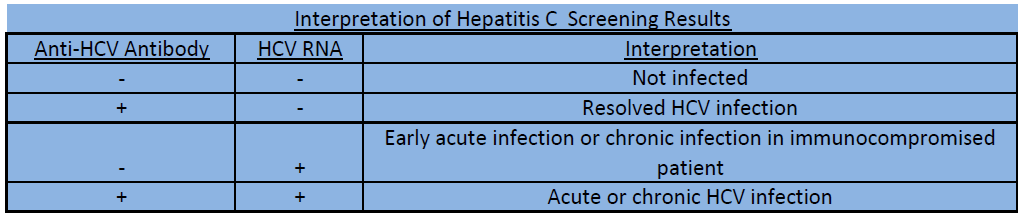
Hepatitis Article

19 Hepatitis C Symptoms, and Transmission & Treatment Information
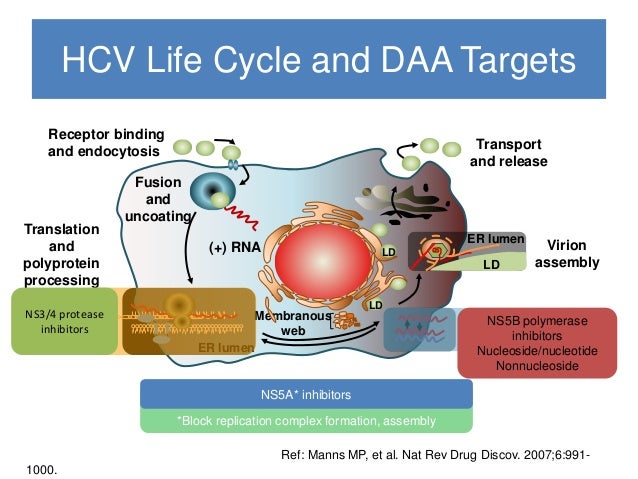
Hep c abhish 27 feb 17.pptx
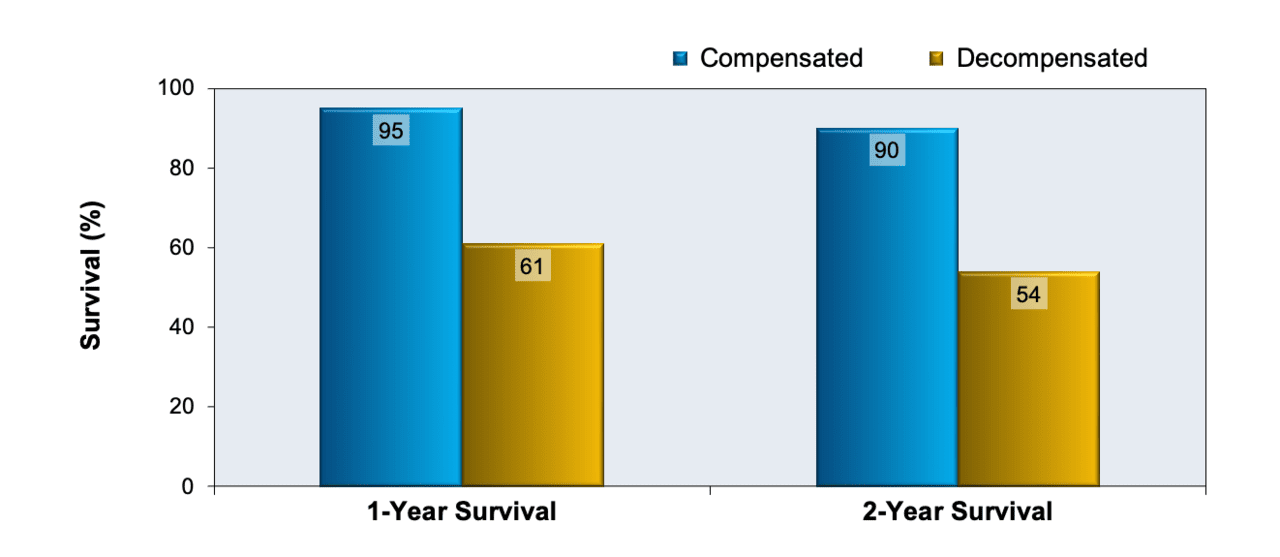
Core Concepts - Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis - Evaluation, Staging, and Monitoring of Chronic Hepatitis C - Hepatitis C Online

Hepatitis C - The Lancet

Advances In Treating Hep C Lead To New Option For Transplant Patients | Kaiser Health News
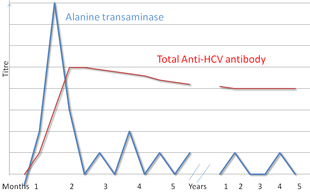
Hepatitis C - Wikipedia

Can You Die from Hepatitis C? Prognosis and Life Expectancy
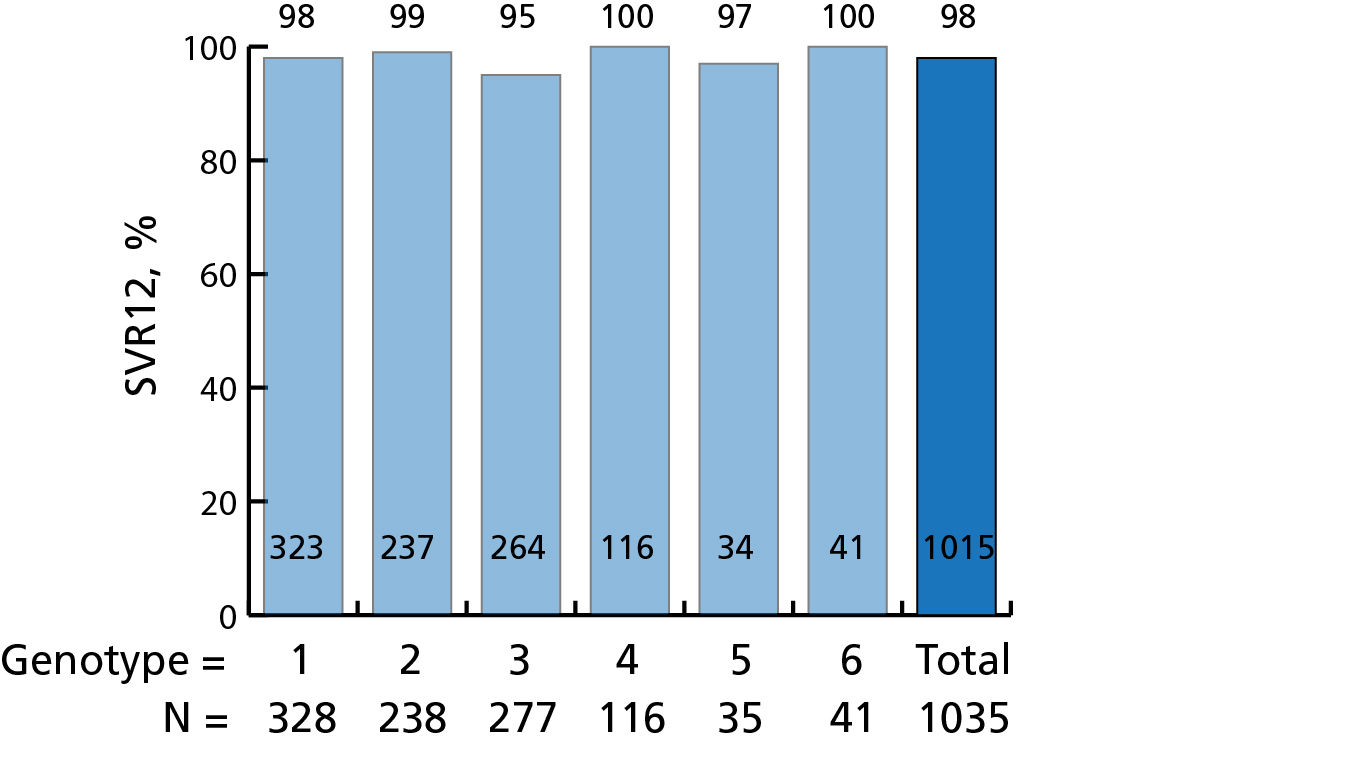
Hepatitis C
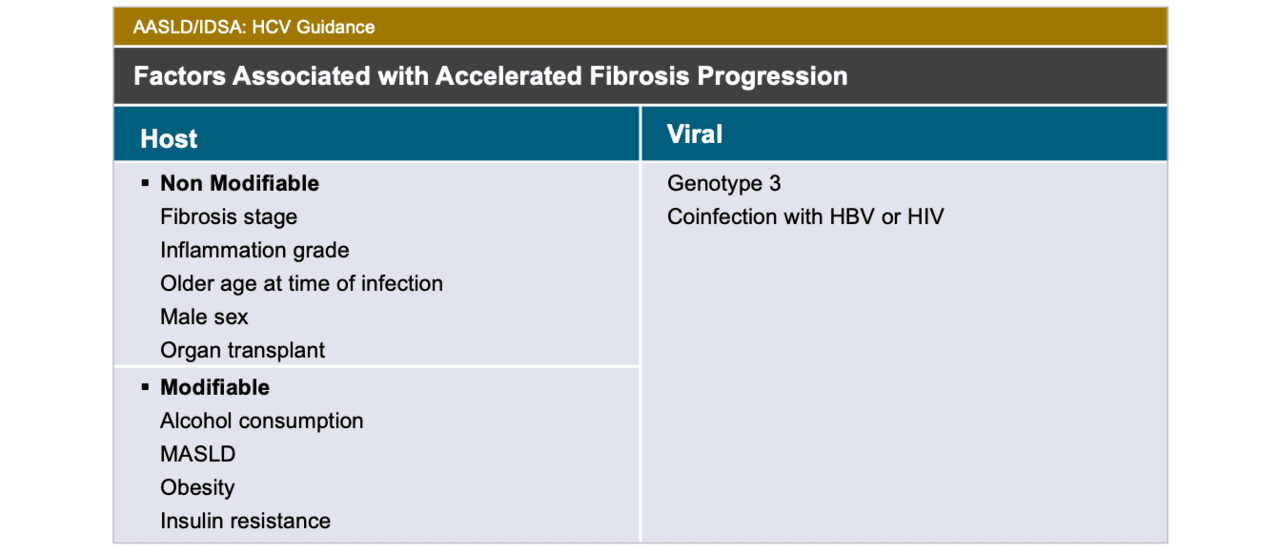
Core Concepts - Making a Decision on When to Initiate HCV Therapy - Evaluation and Preparation for Hepatitis C Treatment - Hepatitis C Online
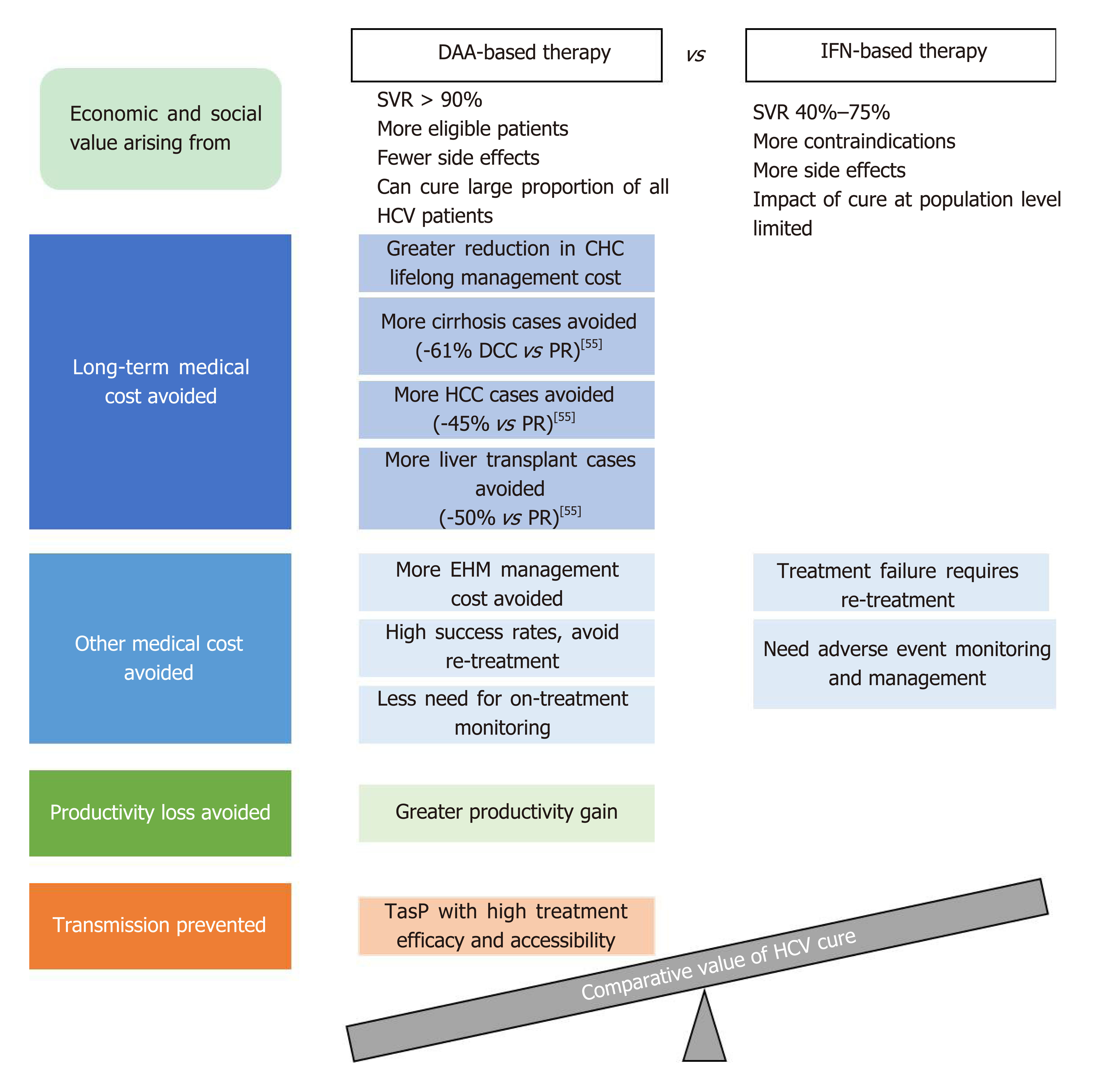
Hepatitis C virus cure with direct acting antivirals: Clinical, economic, societal and patient value for China
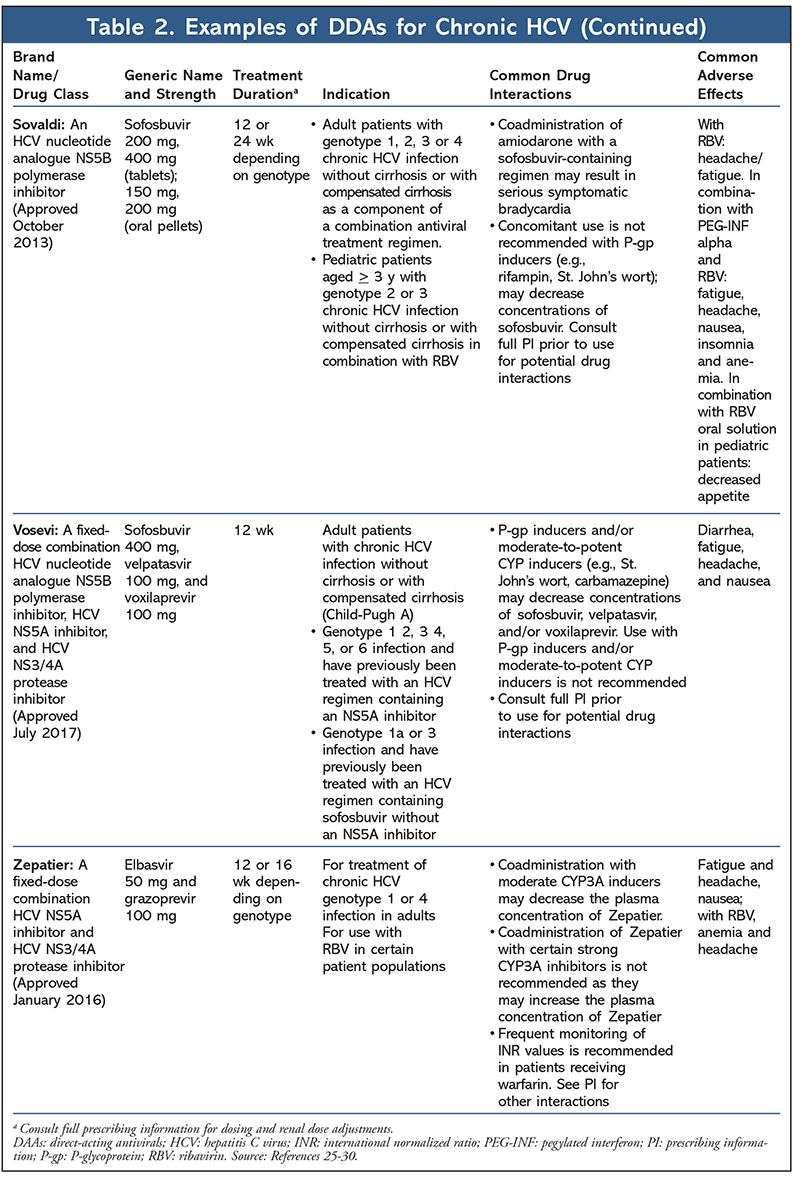
The Pharmacist's Role in Identifying, Treating, and Preventing Chronic Hepatitis C

Kidneys from donors with hepatitis C virus increased recipient life expectancy, reduced costs

Global burden of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in people with hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study - The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Posting Komentar untuk "hep c life expectancy"