 Collection and evaluation of the whole blood clotting test (WBCT). The... | Download Scientific Diagram
Collection and evaluation of the whole blood clotting test (WBCT). The... | Download Scientific DiagramBe sure to remember your password. If you forget, there's no way to StudyStack. to send you a reset link. You'd need to create a new account. We do not share your email address with others. It is only used to allow you to reset your password. For more details read our and . Is he a StudyStack user yet? Study Guide Ch 13Chabner, Medical Language 8th Edition, Chpt 13 Blood System QuestionAnswered white blood cells with reddish granules, INCREASE numbers in allergic eosinopohil reactions Protein threads that form the basis of a FIBRIN clot are "protein yarns" formed by fibrogen. (Don't confuse with the platelets that are "cells" torombins) Method of separation of plasma proteins by electric charge Electroforesis foreign material that invades the antigens of the body pigment produced from hemoglobin when red blood cells are destroyed (hemolisis) bilirubin an undifferentiated blood cell is called hematopotic stem cell (when the stem cells have not yet changed in mature forms are classified "diffrentiated") anticoagulant found in blood heparin - the natural anticoagulant of the body a disorder of the Red Cell MORPHOLOGY is Poikilocytosis (red cells abnormally formed characteristics of several anemias) Deficiency in the number of white blood cells (in this case, a neutrophil deficiency) an immature red blood cell is an eritroblast (erythr/o = red, -blast = immature cell) derived from the myeloid bone marrow (meel = bone marrow, -oid = derivative/replacement) Disaggregation of the receptor's red blood cells when the incompatible blood is mixed hemolysis (hemo = blood, -lysis) Name that ANEMIA! Sideropenia occurs, causing poor production of hemoglobin. iron deficiency anemia (sideropenia - low iron anemia) Name that ANEMIA! Reducing red cells due to excessive cell destruction. hemolytic anemia (hemo = blood, - Lytic = pert to collapse/separation/destruction) Name that ANEMIA! Lack of blood cell production due to the absence of cell formation in the bone marrow. APLASTICA ANEMIA - (plastic = not showing growth or change of structure) (anemia = a condition in which the blood is deficient in red blood cells, in hemoglobin, or in total volume) Name that ANEMIA! Defect inherited in capacity to produce hemoglobin. Thalassemia (aka: Mediterranean anemia ) Name that ANEMIA! Lack of mature red cells - due to - inability to absorb vitamin B12 in the body Pernicious anemia (pernicious = highly injurous or destructive) excessive iron deposits throughout the body hemochromatosis (hem/o = blood, chromat/o = colored, -osis = abnormality) symptoms of pallor, shortness of breath, infection, hemorrhagic gums, predominance of immature and abnormally functional leukocytes, and a low number of mature neutrophils in a small child may indicate a probable diagnosis of acute lymphocytic leukemia (also known as TODOS) marked by an abnormal increase in the number of frontal lymphoblasts, characterized by rapid appearance and progression of this. Excessive hemorrhagia caused by the congenital lack of factor VIII or IX Hemophilia (hem/or = blood, -philiac = pert to a "tendency" towards) Hemophiliac - tends to bleed. Is the venous blood blocked in a test tube to measure... coagulation time (15-20 minutes is the normal range) The blood sample is spilled into a test tube so that red cells fall at the bottom and the percentage of RBC is taken Hematocrite (hemat/or = blood, -crit = count/judge/guage) the blood stain is examined to determine the form or form (morphology) of the cells. Morphology of red blood cells (form/change study) Leukocytes are stained and count under a microscope to see numbers of mature and immature forms of the WBC (differential is the change that occurs when cells mature in their immature forms) venous blood is collected; added anti-coagulant and FALL distance cells in the time period are determined in this test. .. A "Red Blood Cell" (erythr/or = red, cyto = cell) (cell type) "white cell; fagocito, and is a precursor of a macrophageal monocyte" (mon/o = one, single) (-cite = cell, in this case, the kernel) term means "rombocito" platelet term meaning "bone marrow cell; it gives rise to many types of blood cells" Hematopoietic Stem Cell term meaning "leucocyte formed in lymphatic tissue; produces LYMPHOcyte antibodies (produced in lymphatic tissues) term meaning "leucocyte with dense granules, REDDISH; associated with ALLERGIC Esinophil(s) reactions term meaning "leucocyte (poly) formed in the bone marrow and with granules containing NEUTRAL Neutrophil(s) term meaning "leucocyte whose granules have an affinity for the BASIC stain; free histamine and heparin Basofilo(s) about blood blood cells, this is a term for "formed irregularity" poikilocytosis deficiency in numbers of RBCs erythrocytopenia (erythr/o = red, cyt/o = cell, -penia = deficiency) reduction of hemoglobin ("color") Hipochrome (hypo- = decrease, chromium/o = color, -ic = pert to.) increase in the number of SMALL cells Microcytosis (micro = small, cytosis = cell condition) eritremia ( characterized by an increase in the total volume of blood and viscosity and typically accompanied by nasal bleeding, headache, dizziness, weakness, etc.) polycytemia vera increase in the number of LARGE macrocytosis cells (macro- = large, cytosis = cell condition) formation of red cells (such as bone marrow) erytropoiesis (erythr/o = red, -poiesis = formation) destruction of red cell hemolysis (hem/o = blood, -lysis = destruction / separation / decomposition relief, but not healing the palliative deficiency of ALL blood cells pancytopenia (pan- = all, cyt/o = cell, -penia = deficiency) increase in the number of granulocytes; seen in allergic conditions eosinophilia (eosin/or - red, alba, rose) (-filia = attraction, trend, increase of cells) symptoms of the disease is called _________? relapsed MULTIPLE point hemorrhagias (multiple petechia formations) purpura (characterized by purplish discoloration patches resulting from the extravagation of blood on the skin and mucous membranes) the separation of blood in its components is called ? apheresis (-apheresis = extraction, disassembly), generally called plasmapheresis symptoms of disease the patient is missing _______? referral A stained blood stain is examined to determine the shape of the individual red blood cells, this test/examination is called...? RBC Morphology this test measures the percentage of red blood cells in a volume of blood hematocrite this test determines the number of clotting cells per cubic platelet millimeter (this tests the) Ability of venous blood to coagulate in a test tube Coagulation time (this test) measures the speed at which SETTLE erythrocytes out of the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate plasma (this test) Determines the numbers of different types of WBCs the differential WBC (this test) Determines the presence of antibodies in babies of Rh negative women or patients with autoimmune hemolytic anemia COOMBS TEST (this procedure employs) Undifferentiated blood cells of a donor, infused in a patient who is treated by leukemia or aplastic anemia hematopoietic stem cell transplant The time needed for a small puncture wound to stop the bleeding is called ? hemorrhagic time test (procedure where a) the needle is inserted into the bone marrow cavity, and a small amount of bone marrow is aspirated and then examined under the biopsy bone marrow microscope (procedure where) The blood is collected and then re-entered in the same patient Use these flash cards to help memorize the information. Look at the big card and try to remember what's on the other side. Then click on the card to change it. If you knew the answer, click on the green picture Know. Otherwise, click on the red The box is not known. When you have placed seven or more cards in the Don't know box, click "retry" to test those cards again. If you accidentally put the card in the wrong box, click the card to get it out of the box. You can also use your keyboard to move cards as follows: If you are connected to your account, this website will remember which cards you know and do not know for them They're in the same box next time I come in. When you need a break, try one of the other activities listed below flash cards such as Matching, Snowman or Hungry Bug. Although it may feel like you're playing a game, your brain keeps making more connections to information to help you. To see how well you know the information, try the Quiz or Test activity. Come on in! The "Know" box contains: Time elapsed: Retries:
Time required for venous blood to coagulate in a test tube This preview shows page 42 - 52 of 53 pages. Students who saw this also studied Montgomery College• ## ################################################# UniversityCyx13. NEWS Introduction of textbook solutions Copyright © 2021. Of course Hero, Inc. Course Hero is not sponsored or supported by any university or university.

Blood from healthy donors failed to clot normally in plastic syringes... | Download Scientific Diagram
Clotting time - Coagulation of whole blood
Recommendations on venous blood sampling
13 The 20-min whole-blood clotting test (20WBCT) in a clean glass tube... | Download Scientific Diagram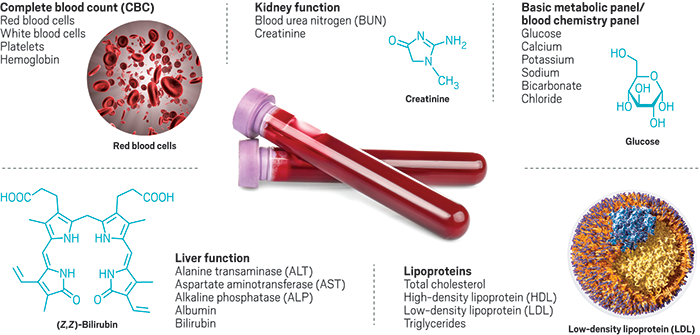
Blood tests at your fingertips
Twenty minutes whole blood clotting test (20WBCT): Glass tubes... | Download Scientific Diagram
WHO | Diagnostic tests and tools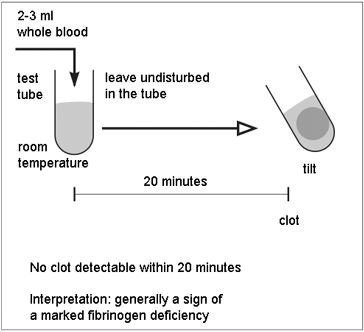
VAPAGuide - Diagnosis of haemostatic defects
Clotted Blood Test Tube Vct Testing Stock Photo (Edit Now) 1212276409
Recommendations on venous blood sampling
VAPAGuide - Diagnosis of haemostatic defects
Tests for hemostasis (Practical) - ppt download
Delayed double reading of whole blood clotting test (WBCT) results at 20 and 30 minutes enhances diagnosis and treatment of viper evenomation
How to perform the 20 Minute Whole Blood Clotting Test (20WBCT)... | Download Scientific Diagram
Early tests to detect blood clots may help save critically-ill Covid-19 patients from stroke - The Economic Times
BDVacutainer Venous Blood Collection Tubes: SST Serum Separation Tubes: | Fisher Scientific
Overview of Blood | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
INR Self-Testing | Blood Clots![Euglobulin Clot Lysis Time [ECLT] Euglobulin Clot Lysis Time [ECLT]](https://practical-haemostasis.com/images/Images-2/Fibrinolysis/eclt_test_tube.jpg)
Euglobulin Clot Lysis Time [ECLT]
VACUETTE® Blood Collection Tubes - Greiner Bio-One
BDVacutainer Venous Blood Collection Tubes: SST Serum Separation Tubes: | Fisher Scientific
Hemolysis - Wikipedia
Blood from healthy donors failed to clot normally in plastic syringes... | Download Scientific Diagram
BD Vacutainer Plus Venous Blood Collection Tube Clot Activator and Gel for Serum Separation - Mountainside-Healthcare.com
Amazon.com: BD 367988 Vacutainer Plus SST Plastic Venous Blood Collection Serum Tube with Red/Gray Conventional Closure, 8.5mL Capacity, 16mm Diameter x 100mm Length (10 Cases of 100): Industrial & Scientific
INR Test | HealthEngine Blog
Vacuette Tube Ven BC 8ml 16x100 Plstc Srm Clt Actvtr/Gl Rd/Ylw 50/Pk - Henry Schein Special Markets
Evacuated Blood Collection Tube, Pro-coagulation Tube, Venous Blood Collection Products China
Preanalytics For Coagulation Testing: Pitfalls And Possible Impact | Omnia Health Insights | News from the global healthcare community
Fibrinogen: Purpose, Procedure & Risks
Thin blood: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Venipuncture - Wikipedia
Blood Bottles Guide | Geeky Medics
BD Vacutainer Venous Blood Collection Tube Guide - Wall Chart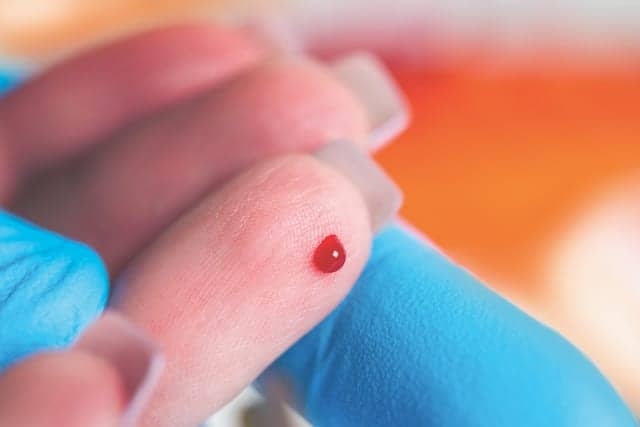
Capillary Blood Sampling - Clinical Lab Products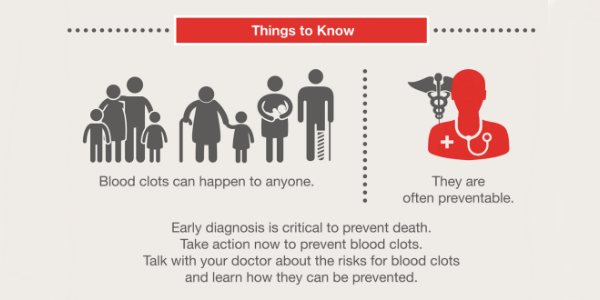
Diagnosis and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism | CDC
Blood Gas, Venous (VBG), Blood* - Rutland Regional Medical Center
Specimen Collection » Laboratory Alliance of Central New York, LLC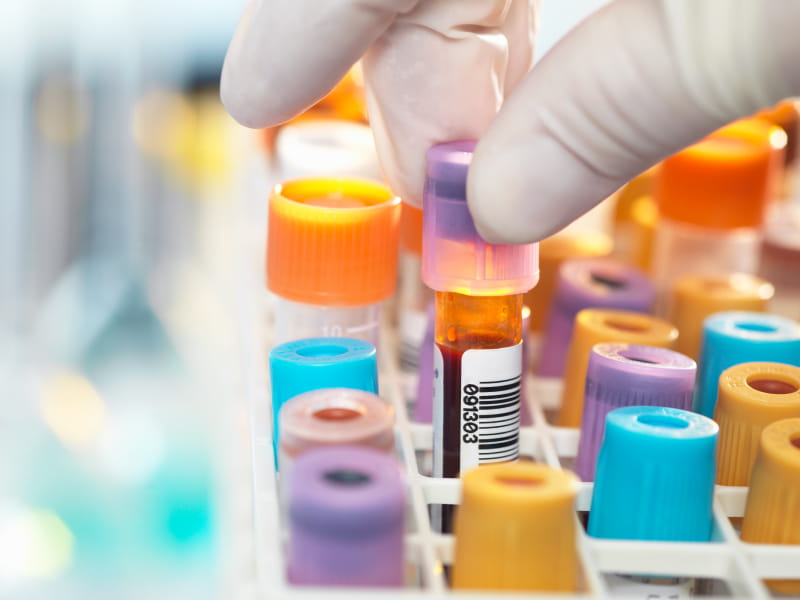
What's blood type got to do with clot risk? | American Heart Association
DVT (Blood Clot In the Leg): 7 Warning Signs and Symptoms
 Collection and evaluation of the whole blood clotting test (WBCT). The... | Download Scientific Diagram
Collection and evaluation of the whole blood clotting test (WBCT). The... | Download Scientific Diagram













![Euglobulin Clot Lysis Time [ECLT] Euglobulin Clot Lysis Time [ECLT]](https://practical-haemostasis.com/images/Images-2/Fibrinolysis/eclt_test_tube.jpg)



















Posting Komentar untuk "test in which venous blood is clotted in a test tube"